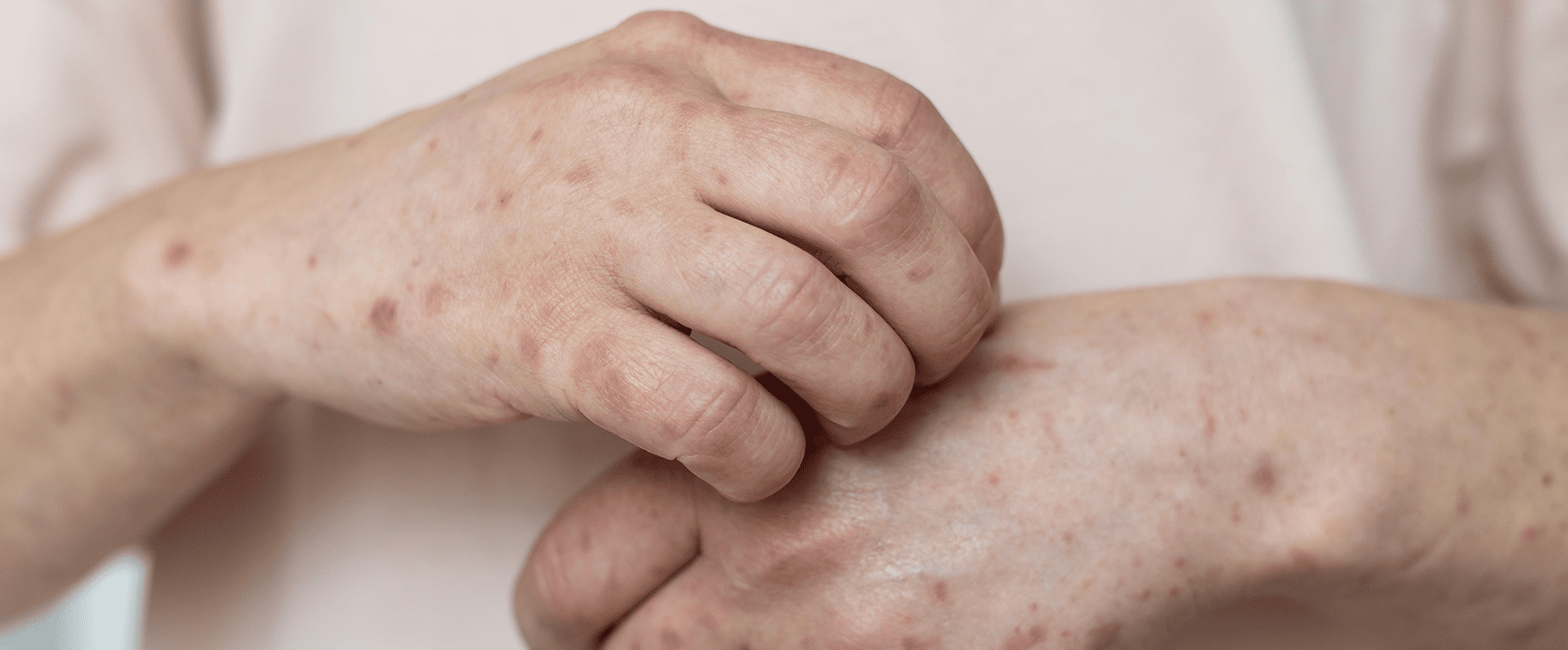
Lupus anticoagulants (LA) are a type of antibodies in an individual’s blood. These antibodies attack healthy cells within the body instead of harmful microorganisms or other invading cells. Phospholipids, an essential component of the cell membrane, are the main target of these antibodies. These antibodies are specific to an immune system disorder called Antiphospholipid Syndrome, also known as Lupus anticoagulant (LA) syndrome. It is a disorder of the immune system that causes an increased risk of blood clots and miscarriages.
Lupus and lupus anticoagulant are not the same. Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease, while lupus anticoagulant is a type of antibody found in the blood that can be an indicator of a blood clotting disorder.
Symptoms of Lupus anticoagulants
The lupus anticoagulant increases the risk of blood clots in an individual’s body. Depending on where the clot has formed, the symptoms can be noticed.
The most commonly associated areas and their related symptoms include:
Brain: Strokes, fatigue, mini-stroke (transient ischemic attack), seizures, involuntary muscle movements, or shaking.
Heart: Chest pain, heart attack, and mitral valve regurgitation.
Lungs: Shortness of breath, sudden chest pain, exhaustion or tiredness, high blood pressure in pulmonary arteries, pulmonary embolism, and sudden death.
Kidneys or stomach: Nausea, bloody stool, fever, thigh pain, diarrhoea, etc.
Legs: Numbness, pain, redness, swelling, warmth, sores, and ulcers.
Others: Other signs and symptoms include patches of discoloured skin, headaches, nausea, discomfort in arms, back, joints, low blood platelet count, skin rashes, tissue death, etc.
In pregnant women, it may cause delayed fetal development, miscarriages, and preeclampsia.
Causes of Lupus Anticoagulant
There is no definitive known cause of lupus anticoagulants in an individual. However, a few risk factors such as infections, medications, and autoimmune conditions such as systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) can result in the development of these antibodies.
A few other triggers that may cause blood clots include:
• Pregnancy
• Cancer
• Smoking
• Hormone therapy
• Birth control pills
• Prolonged bed rest
• Kidney diseases
Diagnosis
The healthcare professional diagnoses antiphospholipid syndrome by:
• Physical examination of an individual
• Asking about symptoms and medical history
• Blood tests
The healthcare professional usually advises blood tests when an individual has unexpected blood clots or has had more than one miscarriage (mothers). There are several tests that are helpful in detecting lupus anticoagulants in an individual’s body, including the ANA (antinuclear antigen) blot test.
ANA Blot
It is a blood test that looks for antinuclear antibodies in an individual’s blood. In general, antibodies are proteins that are produced by the immune system to help fight foreign particles. However, these antinuclear antibodies attack one’s own healthy cells, mistaking them to be foreign and harmful. These are termed antinuclear since they target the nucleus (Centre) of the cells.
Procedure for ANA blot test
A healthcare professional will draw a blood sample by inserting a small needle into a vein in the arm. This is a procedure with negligible risks (slight pain or sting).
Interpretation of results
Results of the ANA blot test are usually given as either positive or negative.
• Positive: Positive results are indicative of the presence of antinuclear antibodies in an individual’s blood. It may mean that the individual is positive for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
• Negative: Negative results are indicative of the absence of antinuclear antibodies in an individual’s blood. It may mean that the individual is unlikely to have SLE.
Having antinuclear antibodies in an individual’s blood doesn’t necessarily mean that they are positive for the condition. If the individual’s results show positive for the test, then it is likely that the healthcare professional may order a few more blood tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options
Individuals who have lupus anticoagulant but do not exhibit any symptoms may not require immediate medical treatment. A person can take preventive measures to avoid potential triggers for blood clots, such as lifestyle changes (avoiding smoking and inactivity).
If an individual shows symptoms of blood clots, treatment aims to prevent blood clots from forming and may include:
Blood-thinning medications
These are the most commonly used medications for treating Lupus anticoagulant. While these blood-thinning agents do not break up already existing clots, they prevent them from getting bigger in size and also prevent formation of new blood clots in the future. Some people may require these medications only for a brief period, while others may require them for a long time.
Plasma exchange
Plasma exchange refers to a procedure where blood plasma containing lupus anticoagulants is separated from other blood cells. The healthy plasma then replaces the plasma that contains lupus anticoagulants.
Prevention
Lupus anticoagulant is an autoimmune condition and cannot be prevented completely. However, making certain lifestyle changes may help lower the risk of blood clot formation. These changes may include:
• Adopting a healthy lifestyle
• Quitting smoking and use of tobacco products
• Exercising regularly
• Avoiding all oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
• Managing other comorbidities such as high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, etc.
Lupus anticoagulant is an autoimmune condition that may cause dangerous blood clots to form anywhere in an individual's body. A healthcare professional diagnoses the condition by physically examining the person for any signs and symptoms of blood clots, along with blood tests. Antinuclear antibody (ANA) blot testing is most commonly used to identify this disease. Blood thinners and lifestyle modifications may help reduce the likelihood of blood clot development and its associated complications.